How does the EQE work?
Starting from 2027, the EQE will consist of a foundation paper (paper F), and four main examination papers (papers M1-M4).
The EQE will undergo a transition to a new system from 2025 to 2027. This transition will fully adapt it to a modular digital examination format.
During these 3 years, there will be a gradual transition into the new system, and the options for candidates will depend on the years of professional activity they will have by the time of the 2025 examination:
i) Candidates having at least 3 years of professional activity by the 2025 examination:
Candidates have the option of proceeding via the current system by taking papers ABCD (see a short description of these papers further below) or entering the new system. This can vary in certain situations depending on whether candidates have passed or failed the pre-examination. Candidates should look at “navigating the EQE format changes” to see the various available options and to decide how to proceed.
ii) Candidates having 2 years of professional activity by the 2025 examination:
Candidates have the option of proceeding via the current system or entering the new system. In the current system, candidates will be exempt from the pre-exam (it will not be held in 2025) and can proceed to take current main examination papers ABCD in 2026 (see a short description of these papers further below). Candidates should look at “navigating the EQE format changes” to see the various available options and to decide how to proceed.
iii) Candidates having 1 year of professional activity by the 2025 examination:
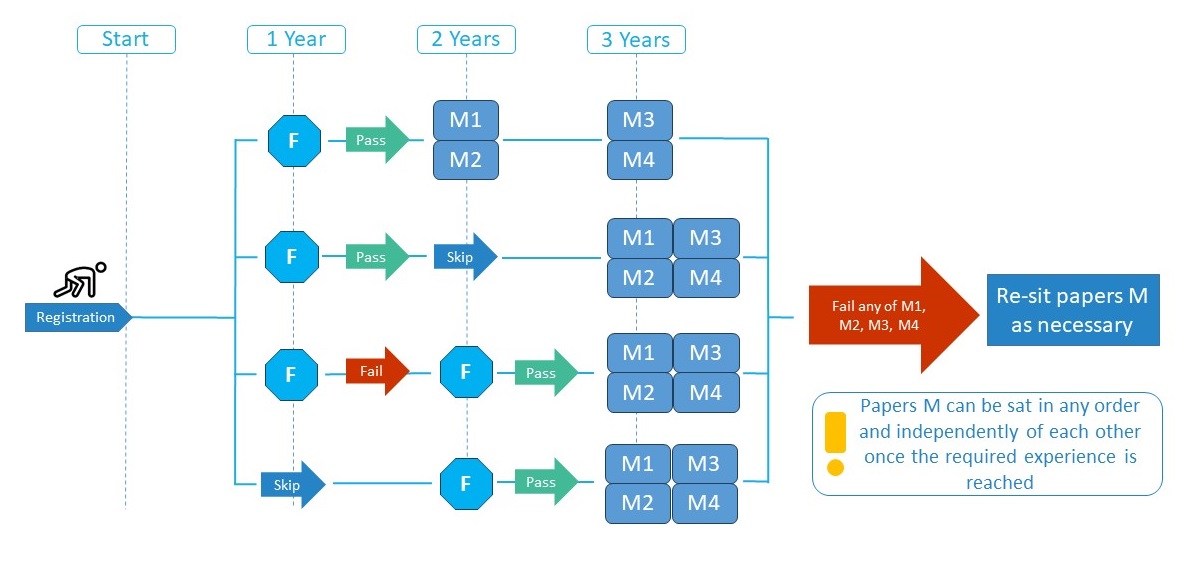
Candidates will automatically start in the new system. They will then have the choice to proceed either via the Standard track or via the Fast track as described below.
Description of the new EQE system and examination papers
New EQE - Standard Track
New EQE - Fast Track%20IPREE).jpg)
Foundation Paper: Paper F
This is the first exam which needs to be passed if you proceed via the Standard track. You can enrol for Paper F after one year of professional activity starting in 2025.
Further information about the setup and content of paper F can be found here.
Main examination: Paper M1
You can enrol for Paper M1 after two years of professional activity and having passed paper F if proceeding via the Standard track, or after three years of professional activity if proceeding via the Fast track. Paper M1 will be available starting in 2026.
Further information about the setup and content of paper M1 can be found here.
Main examination: Paper M2
You can enrol for Paper M2 after two years of professional activity and having passed paper F if proceeding via the Standard track, or after three years of professional activity if proceeding via the Fast track. Paper M2 will be available starting in 2026.
Further information about the setup and content of paper M2 can be found here.
Main examination: Paper M3
You can enrol for Paper M3 after three years of professional activity via the Standard track (having passed paper F) or Fast track. Paper M3 will be available starting in 2027.
Further information about the setup and content of paper M3, can be found here.
Main examination: Paper M4
You can enrol for Paper M4 after three years of professional activity via the Standard track (having passed paper F) or Fast track. Paper M4 will be available starting in 2027.
Further information about the setup and content of paper M4, can be found here.
Description of the main examination papers in the current system
Main examination: Paper A
Paper A is directed at checking your ability to draft a set of claims with an introductory part of a description.
Your aim during this exam is to draft claims which provide the broadest possible protection for an applicant, while at the same time complying with requirements of the EPC such as novelty, inventive step or clarity.
Main examination: Paper B
Paper B is directed at checking your ability to draft a full response to a communication issued by the EPO during examination of a European patent application.
- Your first task is to amend claims is such a way so that the applicant will have the broadest possible protection, while at the same time ensuring that the claims satisfy all requirements of the EPC.
- Your second task is to provide reasoning why the amended claims are patentable over prior art cited in the communication.
Main examination: Paper C
Paper C is directed at checking your ability to draft an opposition to a granted European patent.
- Your task is to draft a notice of opposition while complying with formal requirements for admissibility set out in the EPC.
- Additionally, you have to draft grounds of opposition in order to prove that the granted patent lacks novelty, invective step and possibly has added subject-matter.
Main examination: Paper D
Paper D consists of two parts.
- The first part is aimed at checking your legal knowledge about various aspects of the EPC and the PCT procedures as well as aspects of national law relating to the EPC or the PCT. A crucial aspect of this part is to provide legal basis from the EPC, PCT, etc. in your answers.
- The second part aims at drafting a legal opinion in response to a letter from a client presenting a more detailed state of facts. No basis needs to be provided in your answer.

